Financial Inclusion: Meaning and Barriers
Definition: Financial inclusion is delivery of banking services at an
affordable cost to the vast sections of disadvantaged and low income
group
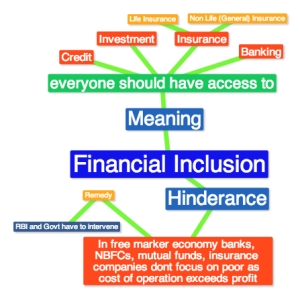
Advantages of Financial Inclusion:
- Turns savings into investment
- Financial Security of family
- Income inequality falls
- Boosts GDP.
- Investment in Agri and allied activities
- Protection from money lenders and Ponzi schemes
- Women empowerment etc. etc.
Steps Taken By Government towards Financial Inclusion
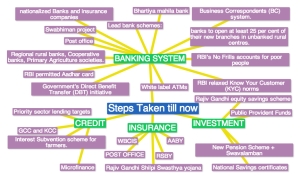 (click image for full screen)
(click image for full screen)
These Steps may have introduced lot of new terms to you, so lets take a look at these measures in detail!
BACKGROUND INFORMATION (banking system)
No-Frills’ Account :
- In the Mid Term Review of the Policy (2005-06), RBI exhorted the
banks to make available a basic banking ‘no frills’ ( frill=unnecessary
features) account
- either with ‘NIL’ or very minimum balances
- With charges that would make such accounts accessible to vast sections of the population.
- The nature and number of transactions in such accounts would be
restricted and made known to customers in advance in a transparent
manner.
‘Simplification of ‘Know Your Customer (KYC)’ Norms :
- Enable those belonging to low income groups without documents of identity and proof of residence to open banks accounts.
- In such cases banks can take introduction from an account holder on
whom full KYC procedure has been completed and has had satisfactory
transactions with the bank for at least six months.
- Some upper cap on deposits and credit is there.
Ensuring reasonableness of bank charges :
- RBI has issued instructions to banks making it obligatory for them
to display and continue to keep updated, in their offices/branches as
also in their website, the details of various services charges in a
format prescribed by it.
White Label ATMs
- Doesn’t have such Bank logo, hence called White label ATMs.
- RBI has given license / permission to non-bank entities to open such ATMs
- Sponsor bank : provides the cash
- White Label ATM company : Rents the place, looks after maintenance and servicing of the machine
- RBI requires White label-ATM companies to install machines in the
ratio of à Two ATMs in (tier 3 to 6 place) : One ATM in (tier 1-2
place). (tier 2 means above 50,000 population )
- Value added services like mobile recharge, utility bill payments etc also available
- value added services plus Selling advertisement space in the room and above the door lead to revenue generation
Business Correspondent (BC) System
- Business correspondents are bank representatives.
- They help villagers to open bank accounts.
- They help villagers in banking transactions. (deposit money, take money out of savings account, loans etc.)
- The Business Correspondent carries a mobile device.
- The villager gives his thumb impression or electronic signature, and gets the money.
- Business Correspondents get commission from bank for every new
account opened, every transection made via them, every loan-application
processed etc.
- NGOs, SHGs,MFIs,Post Offices, Insurance agents, Panchayats, Civil Society Organisations (CSOs) etc. can become BC or banks
- FINO, India’s largest Business Correspondents company
- FINO=Financial Inclusion Network and Operations (FINO).
- It is promoted by various Public and Private sector banks and insurance companies like LIC
Swabhiman Project
- Initiative by the Finance Ministry + Indian Banks’ Association
- launched in 2011
- Make banking facilities available to every habitat with a population >2000 (by March 2012.)
- Banks will provide basic services like deposits, withdrawal, Kisan
Credit Card (KCCs) etc via Business Correspondents (BCs) also known as
Bank Saathi..
- Government will send subsidies and social security benefits (pension etc.) directly to beneficiary’s account.
Background Information (CREDITS)
GCC
- to increase flow of credit to individuals for entrepreneurial activity in the non-farm sector
- All Credit Card (e.g. Artisan Credit Card, Laghu Udyami Card,
Swarojgar Credit Card, and Weaver’s Card etc.) catering to the non-farm
entrepreneurial credit needs of individuals are covered by General
Credit Card Scheme.
- the consumption credit extended to individuals is not be reported under GCC
KCC
- implemented by Commercial Banks , RRBs , and Cooperative
What Are the benefits of KCC:
- It follows a simplified procedure for credit to farmers, a large number of whom are illiterate or poorly educated;
- There is no need to apply for loan every year as KCC provides the
farmers with a credit facility on ongoing basis or revolving credits;
- This allows the farmers to buy seeds, fertilizers and other inputs as per his needs;
- Repayment is allowed after harvest period and thus farmer finds it easier to settle the loan by selling his produce;
- There is a flexibility of drawal of funds from any branch even when he has gone to town for purchase of agricultural inputs
Eligibility:-
- Farmers – Individuals/Joint borrowers (owner cultivators)
- Tenant Farmers, Oral Lessees & Share Croppers
- SHGs or Joint Liability Groups of Farmers including tenant farmers, share croppers etc.
What are the Benefits to Banks
- Work load of rural branches is considerably reduced as there is no need for repeated appraisal and processing of loan papers
- Simplification of documentation and disbursement procedure.
- Reduction in transaction cost to the banks.
- Better Banker – Client relationships
Background (Insurance)
Agricultural Insurance
- National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS): By Agriculture Insurance Company of India Ltd.
- Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme: to insure farmers against adverse weather incidence
Aam Admi Bima Yojna
- landless agricultural families + those involved in 46 other trades
including beedi workers, carpenters, cobblers, fishermen, weavers,
persons with disability employed in different sectors, sweepers,
drivers, anganwadi teachers and members of self-help groups — insurance
benefits under this scheme.
- Besides providing a life cover of Rs. 30,000 for natural death, Rs.
75,000 amount would be paid to the family in case of death due to
accidents.
- If the person covered under the insurance becomes partially
disabled, he will be paid Rs. 37,500 as insurance amount and if the
victim becomes fully disabled he will be paid Rs. 75,000.
- For children : Also, two children in his family will be paid Rs. 100 a month as scholarship.
- Janashree Bima Yojana(launched 2000) was merged with Aam Aadmi Bima Yojana(launched 2007)
Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojna
- Every “below poverty line” (BPL) family holding a yellow ration card
pays INR registration fee to get a biometric-enabled smart card
containing their fingerprints and photographs.
- This enables them to receive inpatient medical care of up to INR 30, per family per year in any of the empanelled hospitals.
- Pre-existing illnesses are covered from day one, for head of household, spouse and up to three dependent children or parents
- The scheme started enrolling on April 1, 2008
Rajiv Gandhi Shilpi Swasthya Bima Yojana
- Comprehensive health insurance scheme for the handicraft artisans across the country.
Post office
- Has tied up with LIC – offering many insurance schemes like Gram Surakha, Suvidha, Sumangal etc.
Background (Investment)
Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme (RGESS)
- Tax saving scheme.
- To attract more people to invest in securities market.
- annual income must be below 12 lakh
- This must be your first investment in securities market
- Money locked in for 3 years
- You must purchase approved shares/mutual funds only.
- For investment upto Rs.50000, you get 50% deduction in income tax.
- You don’t have to pay tax on dividends paid by the company.

